Pineal Gland Eye of Horus. The pineal gland has a romantic history, from pharaonic Egypt, where it was equated with the eye of Horus.
The pineal gland, a little gland around the size of a pea and located in the middle of the brain, is not very large. Melatonin, a hormone produced by this gland, controls when you are awake and asleep. The pineal gland is also referred to as the “eye of Horus” and “third eye.”

The Eye of Horus, often referred to as the udjat, was the Egyptian emblem representing defense, regal authority, and good health. The eye is typically shown in hieroglyphs as a human eye with a falcon’s brow.
Pineal Gland Eye of Horus: What Is It?
A small gland in the brain with a cone-like shape is called the Eye of Horus pineal gland. The production of the hormone melatonin by this gland aids in controlling the body’s sleep-wake cycle. In contrast to light, darkness increases melatonin production.
The Eye of Horus, an ancient Egyptian emblem of power and protection, gave rise to the name of the Eye of Horus pineal gland. An eye with a stylized shape and a curving line across it is a common representation of the eye. This line represents the passage of the sun across the sky.
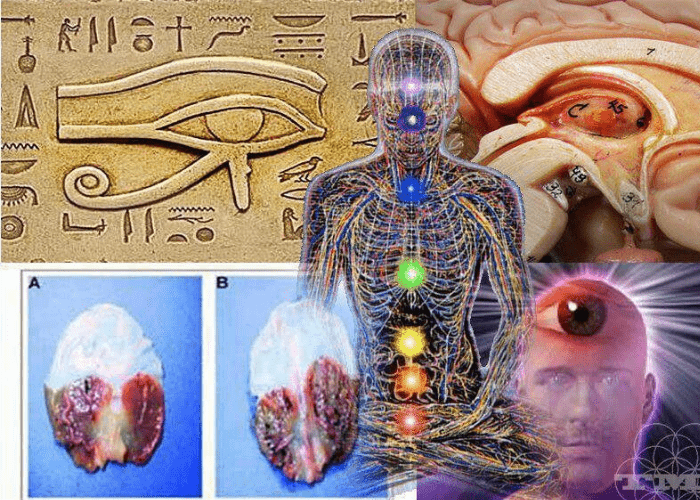
Some claim that the eye of Horus’s pineal gland functions as the third eye or “inner eye” that gives people psychic powers or access to the spiritual world. This assertion is unsupported by any scientific data. But since the gland is directly connected to the visual system, it may assist in explaining why some individuals feel as though their vision changes while they are meditating or praying.
The Pineal Gland in Ancient History
The pineal gland, a small endocrine gland located in the center of the brain, has been recognized and studied in various ancient cultures. In ancient Egypt, the pineal gland was referred to as the “third eye” and was associated with spiritual vision and the ability to see beyond physical reality.
Hinduism also recognized the pineal gland and considered it a spiritual center. In ancient Greece, the philosopher René Descartes referred to the pineal gland as the “seat of the soul.” Despite its recognition in various ancient cultures, the specific functions of the pineal gland were not fully understood until scientific advancements in anatomy and physiology were made in more recent history.
Pineal Gland and the Eye of Horus: What Really Matters
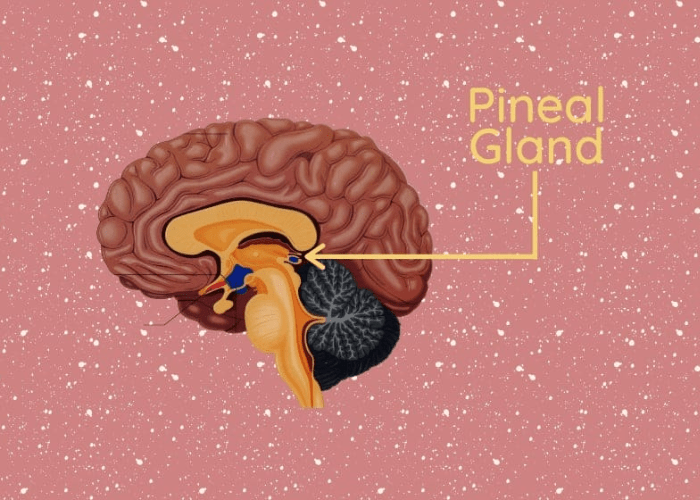
The brain contains the pineal gland, a tiny endocrine organ referred to as the third eye or the eye of Horus. It generates melatonin, a hormone that controls vigilance and sleep.
Because of its likeness to a pinecone, the pineal gland was given that name (pineal comes from the Latin word pinna, meaning “pinecone”). The Egyptians called it the “third eye” or the “eye of Horus” because they thought that this gland held the soul.
Even while the pineal gland’s precise purpose is still not entirely known, we do know that it plays a part in controlling alertness and sleep. It may aid with mood and emotion regulation, according to some experts.
According to some research, the pineal gland may be connected to mystical experiences and psychic abilities. For instance, one study discovered that those who reported having mystical experiences had higher levels of pineal gland activity than those who claimed to have none.
Why is the pineal gland of Horus significant, then? due to the possibility that it is connected to some of the most enigmatic and intriguing parts of the human experience!
Medical Interpretation of the Eye of Horus Pineal Gland
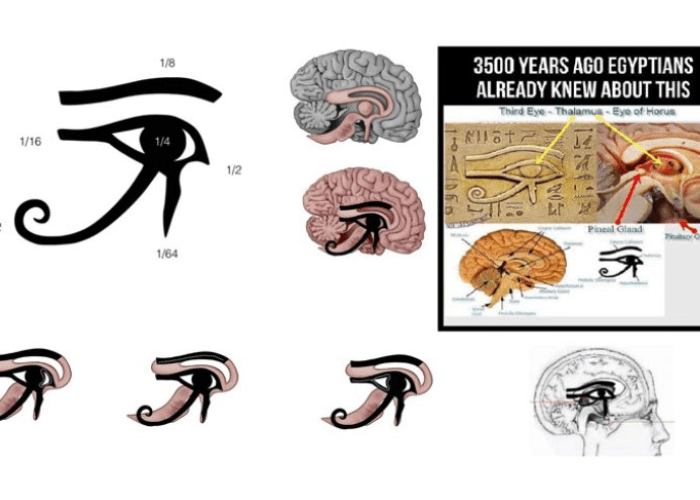
Horus’ pineal gland is known as The Eye of Horus. The eye had a significant role in Egyptian mythology. The “eye” was assumed to stand for understanding and intelligence, while the “nose” was meant to represent strength, courage, and daring. A tiny endocrine gland in animals’ brains called the pineal gland produces the hormone melatonin, which is essential for controlling circadian rhythms (circadian refers to cycles or rhythms).
The lateral commissure (canthus) and the triangular object represent the Eye of Horus’s hearing on the pupil’s left side. The 1/16th of a Heqat is placed in the same location.
- Taste
The primary gustatory lobe of the cerebral cortex interprets a taste signal sent by the thalamus.
- Touch
Touch is a physical feeling that may be felt thanks to the somatosensory pathway, which also transmits information about temperature, awareness of joint and muscle position, light touch, pain, and pressure, among other physical sensations (proprioception).
- Smell
We move beyond the visual domain and investigate the enigmatic elements of the human senses, starting with the sense of smell, in order to show how the Eye of Horus ties to human neuroanatomy.
- Vision
When light enters the retina of the eye, neurons there transmit electrical impulses to the neothalamic adhesion (Massa intermedia), where certain thalamic fibers that transmit vision and other sensations run in the middle before bending laterally to the same thalamus.
- Wisdom
Because of its reputation as a symbol of wisdom or intellect, the Eye of Horus has received a number of metaphorical names, including the Eye of the Mind.
What Greek Term Was Given to the Pineal Gland in the Eye of Horus?
The Horus pineal gland was referred to as the “eye of Horus” by the Greeks. Halfway between the two hemispheres of the brain, the gland is situated in the center. It is three centimeters in diameter and dark blue in hue.
The Egyptians believed that this gland is the source of dreams and that if you have power over your dreams, you will have control over your life. They also thought that a person’s mental state may change if this gland was activated by particular colors (for example green).
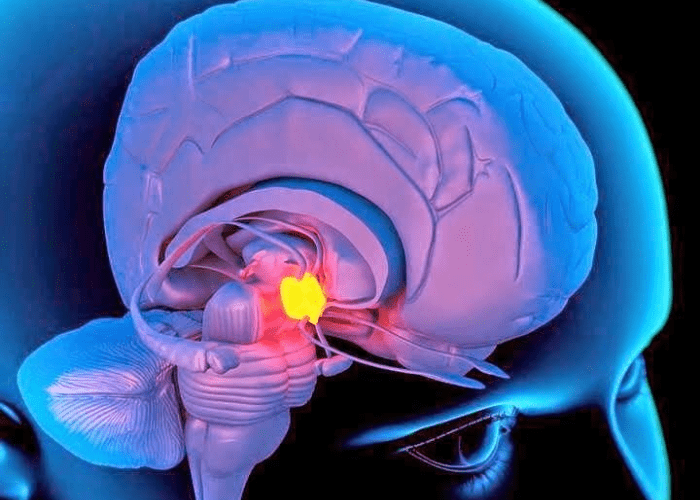
They thought that their soul was contained within the “eye of Horus” in the pineal gland and that the soul would expire if it were harmed or removed. They believed that specific hues, like green, might alter your personality, and that exposure to light or music could induce dreams.
The Greeks considered their deity Apollo as a forerunner of Jesus Christ, and they thought that this gland was connected to him. They thought that since your eyesight wasn’t yet flawless, it had been affected if you had the eye disorder known as amblyopia (lazy eye).
Eye of Horus Compared to the Pineal Gland
The Eye of Horus and the pineal gland are both ancient symbols that have been associated with spiritual and mystical concepts. However, there is no direct comparison between the two as they have distinct origins and meanings.
The Eye of Horus is an ancient Egyptian symbol with a history that spans thousands of years, and it was associated with protection, power, and good health. On the other hand, the pineal gland is a physical structure in the human brain that was recognized and studied by ancient cultures for its role in regulating sleep and wake cycles and its potential association with spiritual experiences.
While both the Eye of Horus and the pineal gland have been connected to spiritual and mystical concepts, the two symbols should not be confused or directly compared as they represent distinct aspects of ancient knowledge and beliefs.





